A Beginners guide to LDAP
The name Lightweight Directory Access Protocol doesn’t directly give even us idea about what this tech is and what it is used for. The first time I was reading it, I was confused because of the jargon words used in the blogs. In this blog I tried explaining the ldap concepts, hope you enjoy it!!

Protocol? Directory? What?
Problem Statement
Every company needs to keep information about the employees like the name, email Id, house location, team etc. They can also use this information to authenticate a user to their internal portals or some services they are using. If a company wants its employees to have access to GCP, Azure, Atlassian and the other services they user, should they create the employee’s account in all of these portals? Also the employee need to learn the password for all those account. Ohoho, that’s a lot of work.
To solve this problem, the company can use OAuth, or any of the Single sign-on protocol, either SAML or LDAP.
In LDAP, you store all these information in a server(referred as ldap server) and send the requests to this server for authentication. This is how a entry in ldap looks like
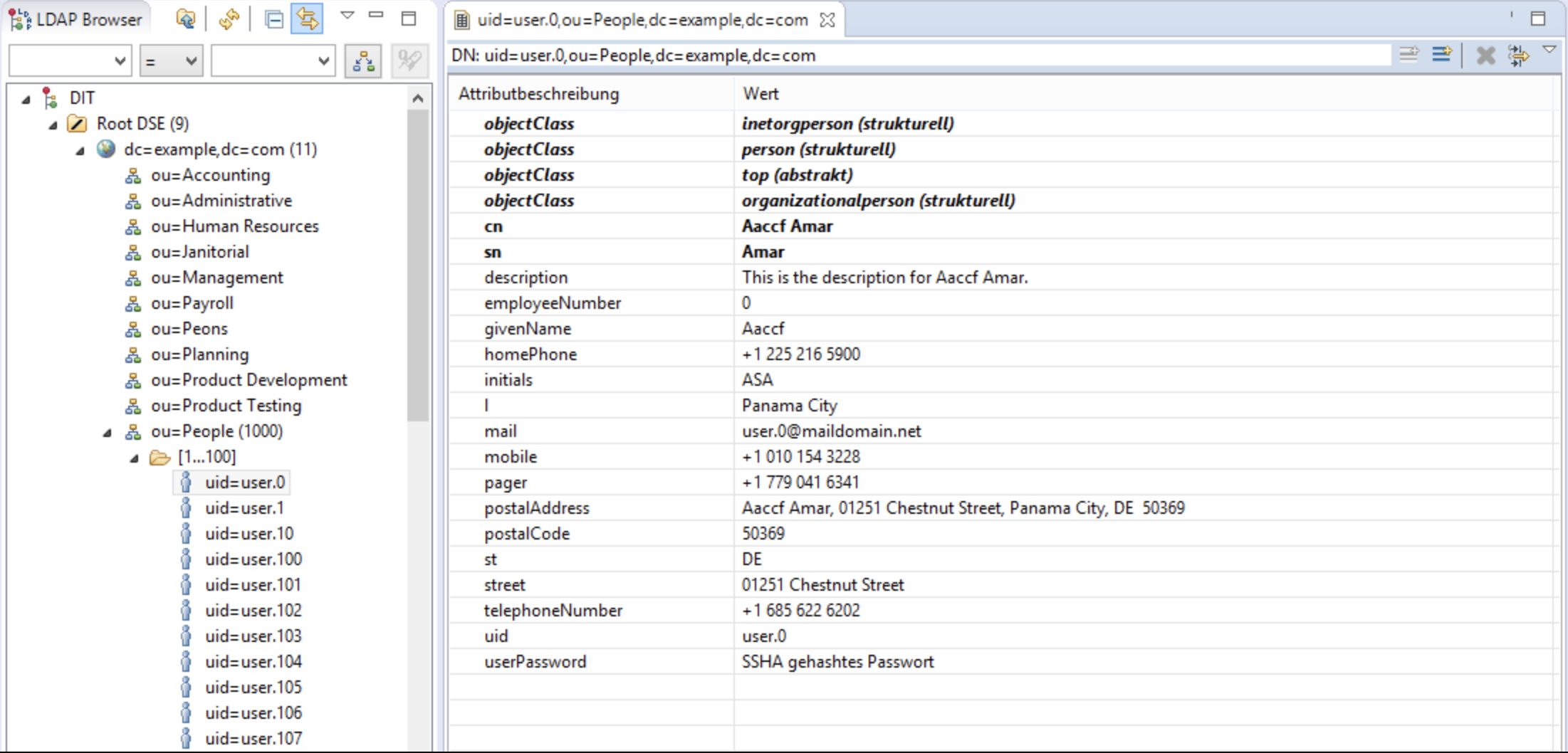
For each user we are storing their employeeNumber, name, phone number, mobile etc. Now lets deep dive into concepts related to ldap.
Key Concepts
The entries in a ldap server is stored in the form of a n-array tree, in the example the node ou=People has all the users as its child. Each node has a dn entry which is equal to the path from that node to the root node.
The field objectClass species the rules which entry must follow, as an example for a class having objectClass=person we can define the rule that all entries must havegivenName and mail and must not contain the teamId.
LDAP allows the user to define the schema for objectClass entries and also the name of the attributes (some company may prefer to store the name of the user in userName, while others can store it in name).
We can query the ldap server to add, modify or delete a entry and also to verify the credentials for a particular user. To view the entries in the ldap directory you can use the Apache Directory Studio.
Commands
The LDAP C-API provides us the command line tool to the ldap operations like authentication, interrogation, update and control.
To keep the blog short I will cover the ldapsearch command in this post, for more commands please use LDAP command line tools. We can user ldapsearch command line utility to query a ldap server. The general format of a ldapsearch query is
ldapsearch <options> -D <bind_DN> -b <base_DN> <searchFilter> <requestedAttributes>
here
- bind_DN is the dn of the user for authentication to the ldap server
- base_DN is the dn of the node from where you want to start searching
- searchFilter is filter to return the required result, so if you searchFilter is “(objectClass=person)” then you will only get those entries containing
objectClass=persionattribute. - Sometimes you don’t need all the attributes of the entry, so to limit those you can give the attributeName in the command.
Example Query:
ldapsearch -LLLxWH ldap://ldap_server.com:389 -D "CN=Deepak,CN=Users,DC=ldap,DC=io" -b CN=Users,DC=ldap,DC=io "&(objectClass=person)(uid=deepak)" cn sn mobile
That’s all the basic concepts of ldap, Thanks for reading the blog!!.
For more detailed tutorial on implementation and key concepts use this link.